Abstract
Context:
The quality of the educational system is considered to be the most important influential factor in universities. Students have different characteristics that affect their academic achievement and failure. The educational failure of medical students has irreparable effects on various individual, social, and economic aspects. The present study aimed to investigate the influential factors in the academic achievement and failure of medical students in Iran.Methods:
This systematic review was conducted through the two-step search of keywords such as “academic achievement” OR “academic failure” AND “medical student” in national and international databases, including SID, Google Scholar, and Scopus, and 32 and 58 articles were extracted from the two database categories, respectively. After reviewing the titles and abstracts, 38 articles were excluded. After the assessment of the remaining full-text articles, 36 other cases were also excluded, and 16 articles were reviewed.Results:
The influential factors in academic achievement and failure included the entrance exam quota type, high school diploma grade, gender, parental education level, occupation status, place of residence, interval between the high school diploma and university admission, indigenousness, grades of the specific course of the entrance exam, socioeconomic status, self-esteem, IQ, young age, competitiveness, effort, social interest, the volume of university courses, exam preparation, the quality of the teacher’s education, level of interest in the course, the importance of the course in the comprehensive exam, and the ability of the teachers. In addition, various individual and family factors, socioeconomic status, and educational facilities have been reported to affect the academic achievement or failure of medical students.Conclusions:
According to the results, the academic achievement and failure of medical students are affected by several factors, which should be considered in medical education.Keywords
1. Context
Every year, universities admit new students and graduate students, and attention to educational quality is paramount in this cycle. Therefore, improving the quality of the educational system is considered to be the most important influential factor in the development of countries (1). The overall structure of medical education in the world is almost identical, without a tangible difference in almost every country. The general medical education agenda in Iran consists of four levels, including basic sciences, physiopathology, pre-internship, and internship. With the respective comprehensive examination of basic sciences and pre-intership exam, the scientific qualifications of the students are evaluated to enter the physiopathology and clinical stages (2).
University professors and students are the pillars of the higher education system and play a key role in the development and growth of the quality of numerous educational and research processes. Therefore, academic education is regarded as the highest level of learning, and in addition to quantitative development, basic steps should be taken toward improving the quality development (3).
Students have different characteristics that affect their academic progress and failure. Progress is the goal that is set by individuals for themselves, which is success in obtaining good grades and satisfaction with the acquired abilities and skills in educational settings. In contrast, academic failure encompasses dropout, repetition of courses, low quality of education and learning, failure of the education system to achieve its primary goals, and even the unemployment of the graduates of an educational center or their professional incompatibility with the employment needs of the community (4).
Academic failure could be assessed based on various criteria, such as unconditioned (average of semester courses < 12), extension of the academic education period, expulsion, semester cancellation, and dropout (5). Furthermore, UNESCO attributes this concept to the repetition of basic sciences courses, early dropout, and diminished educational quality (6). Due to the quantity development of universities in recent years, academic failure is a major issue that is gradually exacerbated (7), as well as an important challenge in the educational system, which directly and indirectly causes noticeable damage to the individual, family, and the community (8). Reports are indicative of academic failure in approximately 50% of university students within the first year of admission (9).
Several factors may lead to academic failure, such as age, gender, scientific background, motivation and interest in the field, marital status, occupation status, place of residence, parental employment and education level, financial ability, length of the study hours, and addiction. Among the other influential factors in academic failure are drug abuse, dissatisfaction, loneliness, expectation of success, physical and mental health, lifestyle, depression, poor communication with friends and long interval between the high school diploma to university admission, intelligence and talent, indigenousness, grade point average (GPA), admission quota in college/university entrance exam, self-esteem, anxiety, family circumstances and background. These variables are closely correlated, and the exact effect of each on academic failure cannot be clarified (10-12).
Academic failure of students is not a personal problem, but rather a social issue; therefore, fundamental steps must be taken toward addressing the issue. Another important matter in this regard is the academic failure of some medical students due to job sensitivity and its role in the health maintenance of the community as graduate medical students will have poor performance in clinical settings following academic failure. In some cases, the consequences may be irreparable (13) and impose a great economic burden on the community. In social terms, academic failure leads to the production of inefficient skilled labor and ultimately lowers the quality of care services. Individually, academic failure may cause poor communication with the environment and low social self-esteem, and depression or other mental health issues (14, 15).
In a study conducted on the subjects who committed suicide or threatened to commit suicide, academic failure was reported to be the most common cause of suicide, and social issues were the most common cause of suicide threats (16). International studies have also been focused on factors such as poor socioeconomic status, ethnic minorities, gender, and low grades in specific courses during high school, which have been reported to significantly affect academic failure in university students (14, 17, 18). Regarding the criteria for academic achievement and failure, researchers have mostly agreed on the criteria for academic failure and considered academic failure at the GPA of below 12, which is a conditional equivalent (19-22); however, components such as the repetition of courses and lower grades than the acceptable level have also been denoted as important in this regard (23-25). There is disagreement regarding the definition of academic success, including the GPAs of ≥ 16 (unconditioned) (22), GPAs of > 15 (unconditioned) (19), and GPAs of 16 (20) or 17 (21).
The present study aimed to investigate the influential factors in the academic achievement and failure of medical students in Iran.
2. Methods
This systematic review was conducted by searching in national databases (SID) and international databases (Google Scholar and Scopus) for the articles regarding the influential factors in the academic achievement and failure of medical students. Initially, 32 articles were extracted using various MeSH keywords, such as “academic achievement” AND “medical student”, and by using the keywords “academic failure” AND “medical student”, 58 more articles were retrieved.
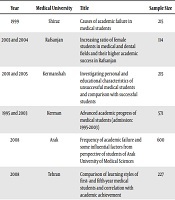
After reviewing the titles and abstracts, 38 articles were excluded. The exclusion criteria were the studies not focused on the academic achievement/failure of medical students and articles conducted at universities other than medical universities. At the next stage, the remaining full-text articles were reviewed, and 36 other articles were excluded due to the lack of the meticulous assessment of the components involved in academic failure and progress or the general assessment of medical students separated by the field of study. Finally, 16 articles were selected and reviewed (Table 1).
Specifications of Reviewed Studies
| Authors | Type of Study | Year | Medical University | Title | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dehbozorgi (22) | Descriptive cross-sectional | 1999 | Shiraz | Causes of academic failure in medical students | 215 |
| Rashidi-Nejad et al. (21) | Descriptive cross-sectional | 2003 and 2004 | Rafsanjan | Increasing ratio of female students in medical and dental fields and their higher academic success in Rafsanjan | 114 |
| Khazaei et al. (19) | Case-control | 2001 and 2005 | Kermanshah | Investigating personal and educational characteristics of unsuccessful medical students and comparison with successful students | 215 |
| Haghdoost et al. (26) | Cohort | 1995 and 2003 | Kerman | Advanced academic progress of medical students (admission: 1995-2003) | 571 |
| Changizi Ashtyani and Shamsi (27) | Descriptive-correlational | 2008 | Arak | Frequency of academic failure and some influential factors from perspective of students of Arak University of Medical Sciences | 600 |
| Moayyari et al. (28) | Descriptive-analytical | 2008 | Tehran | Comparison of learning styles of first- and fifth-year medical students and correlation with academic achievement | 227 |
| Yousefi et al. (29) | Cross-sectional correlational | 2008 | Esfahan | Correlation of academic motivation and academic achievement in medical students | 244 |
| Amrai et al. (30) | Cross-sectional correlational | 2010 | Tehran | Correlation of academic motivation and academic achievement | 244 |
| Asadpour et al. (25) | Descriptive cross-sectional | 2009 | Rafsanjan | Investigating some influential factors in results of comprehensive examination of basic medical sciences from perspective of medical students admitted during 2005-2009 | 160 |
| Ghaibi et al. (23) | Descriptive cross-sectional | 2008 and 2009 | Urmia | Rate of academic failure and underlying factors in medical students | 176 |
| Tagharrobi et al. (31) | Descriptive cross-sectional | 2003 and 2006 | Kashan | Causes of course repetition, conditional, and delayed graduation in medical sciences graduates | 586 |
| Namdari et al. (32) | Descriptive-analytical | 2008 and 2009 | Lorestan | Investigating influential factors in results of comprehensive examination of basic sciences in medical students | 102 |
| Chinipardaz et al. (33) | Descriptive-analytical | 2008 and 2009 | Tehran | Study of emotional intelligence and its association with academic achievement in medical students | 62 |
| Sadeghi Movahed et al. (20) | Case-control | 2013 | Ardabil | Individual and environmental influential factors in academic achievement of medical students | 200 |
| Bijari and Abassi (34) | Descriptive cross-sectional | 2005 and 2008 | Birjand | Predictive validity of comprehensive basic sciences exam for academic success of medical students | 145 |
| Eskandari et al. (24) | Descriptive cross-sectional | 1999 and 2009 | Zanjan | Processes of academic failure of medical students and impact of demographic factors | 894 |
3. Results
After examining the articles, the factors with a positive effect on academic achievement and the factors causing academic failure were determined, which are classified as positive and negative.
3.1. Influential Factors in Academic Achievement
The influential factors in academic achievement included individual and environmental factors, such as regional quotas, diploma GPA of above 16, short interval between high school graduation and university admission, special course grades and language course grades in the university entrance exam, having no jobs, private housing, being single, having a study schedule, interest and motivation, high school GPA, female gender, young age, being native, high self-esteem, IQ of above normal, lack depression, search competition, effort, exam preparation, interest in the course, time to prepare for the entrance exam, higher education than parental diplomas, favorable socioeconomic status, course volume, end-of-semester score of each course, teacher’s educational quality, the importance of the course in the comprehensive exam, teacher’s use of audio-visual and laboratory equipment, and the educational facilities of the institution.
Other individual and environmental factors have also been classified under the same category, such as special quota (war veterans/martyrs) in the university entrance exam, diploma GPA of below 16, long interval between obtaining the high school diploma and university admission, parental education level of high school diploma and below, male gender, marital status, having an extra job, dormitory accommodation, absence in classes, history of admission at other universities, non-nativity, old age at the time of university admission, poor socioeconomic status, low self-esteem, normal IQ, and depression.
3.2. Definition of Academic Achievement
According to the literature, most students with GPAs of > 16 (without conditioned), some with GPAs of > 15 (without conditioned), those with GPAs of A (17-20), and those with basic sciences and introspection grades of 17 - 20, mostly constitute the top students in comprehensive and entrance exams.
3.3. Definition of Academic Failure
Students with the GPA of < 14 and more than one conditional semester, rejection (scores of < 10 in basic sciences and 12 in clinical sciences), late graduation, repetition of courses, and delayed in graduation are examples of students with academic failure. Table 1 shows the specifications of the reviewed articles.
4. Discussion
According to the results of the present study, the most important influential factors in academic achievement were the type of admission to the university via the entrance exam, diploma GPA, gender, time interval between high school graduation and university admission, parental education level, having an extra job, place of residence, absence in classes, marital status, non-nativity, score of special entrance exam courses, old age at the time of university admission, history of passing course in other universities, course volume, IQ, socioeconomic status, competitiveness, effort, preparation and time allocation to exams, interest in the course, quality of teachers’ methods, the importance of the courses in the comprehensive exam, and use of audio-visual and laboratory equipment by teachers.
Student admission method (type of quota) via the entrance exam was observed to be an important influential factor in academic achievement and failure. According to the reviewed studies, the use of other quotas than those dedicated to war veterans and martyrs plays a key role in the academic failure of medical students (19-21, 25). On the other hand, the use of regional quotas (1-3) in the national university entrance exam has been associated with academic achievement (19, 21). Only in one study regarding the clinical level of medical students, the admission method to university (quota classification) was reported to have no effect on academic failure or achievement (24), which could be due to the nature of the clinical courses in medicine and rarity of academic failure.
In several studies, male gender has been reported to be an important influential factor in academic failure (21, 23, 25, 31), while some studies have considered gender to be unrelated to educational status (22, 26, 28, 32). On the other hand, several studies (21, 23, 25, 34) have reported the female gender to be an influential factor in academic achievement.
According to the literature, marriage affects the academic failure of medical students, while being single could result in academic achievement (19-21). In a study, marital status was observed to be an influential factor in course repetition although it was not significantly associated with delayed graduation and conditionality (20). Other studies (22, 24) have indicated that marital status has no significant association with academic failure or achievement, which could be due to the smaller sample size and differences in the course levels of students compared to other studies.
In the reviewed studies, old age upon university admission was reported to be a cause of the academic failure of medical students, while young age led to academic achievement (21, 22). In addition, the long interval between high school graduation and university admission has been observed to be a cause of academic failure, while the short interval between these events has been shown to result in academic achievement (19-21). In some studies, age and the time interval between high school graduation and university admission have been reported to have no significant associations with educational status (26, 28, 32, 33), which could be attributed to the small sample size in these studies.
In some studies, employment has also been identified as an influential factor in the academic failure of university students, while the lack of employment has been introduced as an influential factor in academic achievement (21, 33). On the same note, dormitory residence has been reported to cause academic failure, while nativity and private housing have been shown to prompt academic achievement in medical students (19, 22). Moreover, non-nativity has been reported to affect course repetition, whereas no significant correlation has been observed between the nativity and non-nativity of students with delayed graduation and conditionality (20).
According to the obtained results, lower high school diploma GPA is an influential factor in academic failure, while the GPA of > 16 could result in academic achievement (23). In addition, the parental education level of below high school diploma has been reported to cause academic failure, while the higher education level of parents has been shown to prompt the academic achievement of medical students (19-21). In a study conducted on clinical medical students, parental education level was reported to have no significant impact on the educational status of students (24). Several years of being away from the family since university admission and increased age may naturally diminish the impact on the family environment.
According to the current review, absenteeism in classrooms could lead to the academic failure of students (24). Attending the clinical setting and patient observation are of particular importance to medical students, and absence in university classes (especially clinical courses) leads to academic failure since the content of these courses is mostly practical, and catching with the lessons would be challenging in case of absence. However, absence in basic sciences courses could be partially compensated for by preparing booklets or reference books, which in turn prevents evident academic failure without a significant effect on educational status (19). Admission to other universities has also been considered an influential factor in the conditionality and delayed graduation of students (20). In a research in this regard, the number of the semesters in other universities was reported to have no significant effect (28), which could be due to the impact of other parameters (28).
According to the current review, among the other influential factors in academic achievement were the GPA of all the basic sciences and clinical courses, competitiveness, effort, and social interest, which positively affect academic achievement (30). On the other hand, academic motivation, learning time, and family environment have been shown to have no effects on the success of students, while only cognitive behavior has been reported to prompt success in exams (27). Academic achievement in medical students is also influenced by exam preparation, the importance of basic sciences courses in the final comprehensive exam, quality of the teacher’s educational methods, and use of audio-visual and laboratory equipment by the teachers (28).
5. Conclusions
Several factors affect the academic achievement of medical students, some of which have a definite effect, and some have a relative effect, so that their effect could be strengthened and weakened depending on other parameters. Therefore, the identification of these factors could contribute to proper educational planning to improve the quality of education and prevent academic failure and the subsequent loss of economic and social capital.
Acknowledgements
References
-
1.
Hazavehei SMM, Fathei Y, Shamshirei M. Study on the causes of students' academic probation in Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, 2001-2002. Strides Develop Med Educ. 2006;3(1):33-42.
-
2.
Roudbari M, Sheibak A. The survey of the result and the associated factors in the pre internship examination at Zahedan University of Medical Sciences in September & Mars 2001. Zahedan J Res Med Sci. 2006;1(1):19-27.
-
3.
Rahimi PS, Heshmati H, Moghaddam Z. Survey the Frequency and Risk factors in the Academic Failure in Students that living in dorms of Golestan University of Medical Sciences & Health Sciences in Year 2011-2012. J Torbat Heydariyeh Univ Med Sci. 2014;2(1):16-27.
-
4.
Abadi B, Zamani GH. Factors affecting agricultural students' academic achievement: a case of college of agriculture, Shiraz University. Iran Agricult Extension Educ J. 2010;5(2):31-44.
-
5.
Motlagh ME, Elhampour H, Shakurnia A. Factors affecting students' academic failure in Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences in 2005. Iran J Med Educ. 2008;8(1):91-9.
-
6.
Izadi Sabet F, Ghavami H, Hesam M, Abasian M, Goghataei MJ, Abbasnejad AA, et al. Factors affecting academic failure in region II medical universities students. J Paramed Sci. 2016;6(2):53-8.
-
7.
Esmaeilpour-Bandboni M, Naderi Shad S, Kobrai F, Gholami-Chaboki B. Students’ Viewpoints about Academic Failure and Some Related Factors in Guilan University of Medical Sciences. Res Med Educ. 2017;9(3):72-65. https://doi.org/10.29252/rme.9.3.73.
-
8.
Tovar E, Simon MA. Academic Probation as a Dangerous Opportunity: Factors Influencing Diverse College Students' Success. Community Coll J Res Pract. 2007;30(7):547-64. https://doi.org/10.1080/10668920500208237.
-
9.
Lopez-Barcena J, Gonzalez-de Cossio Ortiz M, Avila-Martinez I, Teos-Aguilar O. [Epidemiological health factors and their relationship with academic performance during the first year of medical school. Study of two generations]. Gac Med Mex. 2009;145(2):81-90. [PubMed ID: 19518013].
-
10.
Neumann M, Edelhauser F, Tauschel D, Fischer MR, Wirtz M, Woopen C, et al. Empathy decline and its reasons: a systematic review of studies with medical students and residents. Acad Med. 2011;86(8):996-1009. [PubMed ID: 21670661]. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACM.0b013e318221e615.
-
11.
Holt MP. Student retention practices in associate degree, entry-level dental hygiene programs. Am Dent Hygienists' Assoc. 2005;79(3):6.
-
12.
Dehghani MR, Haghdoost AA, Talebian E, Zareshahi R, Pourkhandani E, Pourkhandani A, et al. The Concept of Educational Achievement and its Effective Factors according to the Overseas Graduates Point of View: a Qualitative Study. Strides Develop Med Educ. 2010;6(2):99-109.
-
13.
Rahimi B, Jabbari N, Rahmatnejad L, Mohammadpour Y, Kazemi N. Evaluation of the factors affecting students’academic failure in urmia university of medical sciences in 1390. J Urmia Nurs Midwifery Fac. 2013;11(8):614-21.
-
14.
O'Neill LD, Wallstedt B, Eika B, Hartvigsen J. Factors associated with dropout in medical education: a literature review. Med Educ. 2011;45(5):440-54. [PubMed ID: 21426375]. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2923.2010.03898.x.
-
15.
Najafipour S, Yektatalab S. The prevalence depression and relationships with academic failure on students of jahrom university medical science. Pars Jahrom Univ Med Sci. 2008;6(3):27-37. https://doi.org/10.29252/jmj.6.3.4.27.
-
16.
Meilman PW, Pattis JA, Kraus-Zeilmann D. Suicide attempts and threats on one college campus: policy and practice. J Am Coll Health. 1994;42(4):147-54. [PubMed ID: 8132937]. https://doi.org/10.1080/07448481.1994.9939662.
-
17.
Woo JK, Ghorayeb SH, Lee CK, Sangha H, Richter S. Effect of patient socioeconomic status on perceptions of first- and second-year medical students. CMAJ. 2004;170(13):1915-9. [PubMed ID: 15210639]. [PubMed Central ID: PMC421718]. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.1031474.
-
18.
Haidinger G, Frischenschlager O, Mitterauer L. Prediction of success in the first-year exam in the study of medicine--a prospective survey. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2005;117(23-24):827-32. [PubMed ID: 16437320]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-005-0477-x.
-
19.
Khazaei M, Rezaei M, Khazaei S. Survey of personal and educational characters in unsuccess medical students in compare with success students. Koomesh. J Semnan Univ Med Sci. 2008;9(2):87-92.
-
20.
Sadeghi Movahed F, Molavi P, Samadzadeh M, Shahbazzadegan B, Yousefi K. The study of individual and environmental factors affecting achievement of Ardabil medical students. J Health Care. 2013;15(3):47-38.
-
21.
Rashidi-Nejad HR, Mortazavi SMJ. Increased female/male student ratio and the higher academic achievement of the female students of Rafsanjan University of Medical Sciences in academic year 2003-2004. J Rafsanjan Univ Med Sci. 2005;4(3):180-5.
-
22.
Dehbozorgi GH. A survey on dropout risk factors among medical students, Shiraz Medical University, 1999. J Babol Univ Med Sci. 2003;5(5):74-8.
-
23.
Gheibi S, Mohammad Loo R, Moosavi Vaezi SJ, Yekta Z, Pour Ali R, Kafili M. Academic failure and its underlying factors in medical students of Urmia University of Medical Sciences. Strides Develop Med Educ. 2011;7(2):141-6.
-
24.
Eskandari M, Hojati A, Kolifarhood G. Trends of Academic Failure and Its Demographic Determinants among Medical Students in Zanjan University of Medical Sciences. Iran J Med Educ. 2014;14(2):174-83.
-
25.
Asadpour M, Sheikh Fathollahi M, Rezaeian M, Jafari Naveh H, Mahboobi Rad M, Amir Afzali I. A Survey on Factors Affecting the Results of Comprehensive Examination of Medical Basic Sciences in 2005 to 2009 Groups of Medical Students from the Students’ Viewpoints in Rafsanjan University Medical Sciences. J Rafsanjan Univ Med Sci. 2016;14(12):1073-84. eng.
-
26.
Haghdost AA, Esmaili A. Academic achievement of medical students entering 1995-2003. J Med Educ Develop. 2008;5(2):87-0.
-
27.
Changizi Ashtyani MA, Shamsi SM. Frequency of educational decline and some effective factors of student’s opinion in Arak University of Medical Sciences. Arak Medical University Journal.
-
28.
Moayyari A, Sabouri Kashan AI, Gharib M, Biglerokhani M. Comparing the learning styles of first and fifth year students in medicine and its relationship with academic achievement. J Med Educ Stud Develop Center. 2009;6(2):110-8.
-
29.
Yousefi A, Ghasemi G, Firooznia S. The relationship between academic motivation and medical students' academic achievement. Iran J Med Educ. 2009;9(1):79-85.
-
30.
Amrai K, Motlagh SE, Zalani HA, Parhon H. The relationship between academic motivation and academic achievement students. Proced Soc Behav Sci. 2011;15:399-402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.03.111.
-
31.
Tagharrobi Z, Masoudi Alavi N, Fakharian E, Mirhoseini F, Rasoulinejad SA, Akbari H, et al. Frequency and predictors of courses repetition, probation, and delayed graduation in kashan faculty of nursing and midwifery. Nurs Midwifery Stud. 2013;2(4):89-96. [PubMed ID: 25414885]. [PubMed Central ID: PMC4228902]. https://doi.org/10.5812/nms.9920.
-
32.
Namdari P, Ebrahimzadeh F, Mardani M. Study of effective factors on comprehensive test of basic medical sciences of the medical students of Lorestan university of medical sciences. Sci Mag Yafte. 2010;12(1):5-12.
-
33.
Chinipardaz Z, Ghafourian Boroujerdni M, Pasalar P, Keshavarz A. Investigation of emotional intelligence and its relationship with academic achievement in medical students of Tehran University of Medical Sciences in 2008-2009. Strides Develop Med Educ. 2012;8(2):167-72.
-
34.
Bijari B, Abassi A. Predictive validity of comprehensive basic science examination for medical students’ academic performance in Birjand University of Medical Sciences. Iran J Med Educ. 2014;13(12):1011-8.